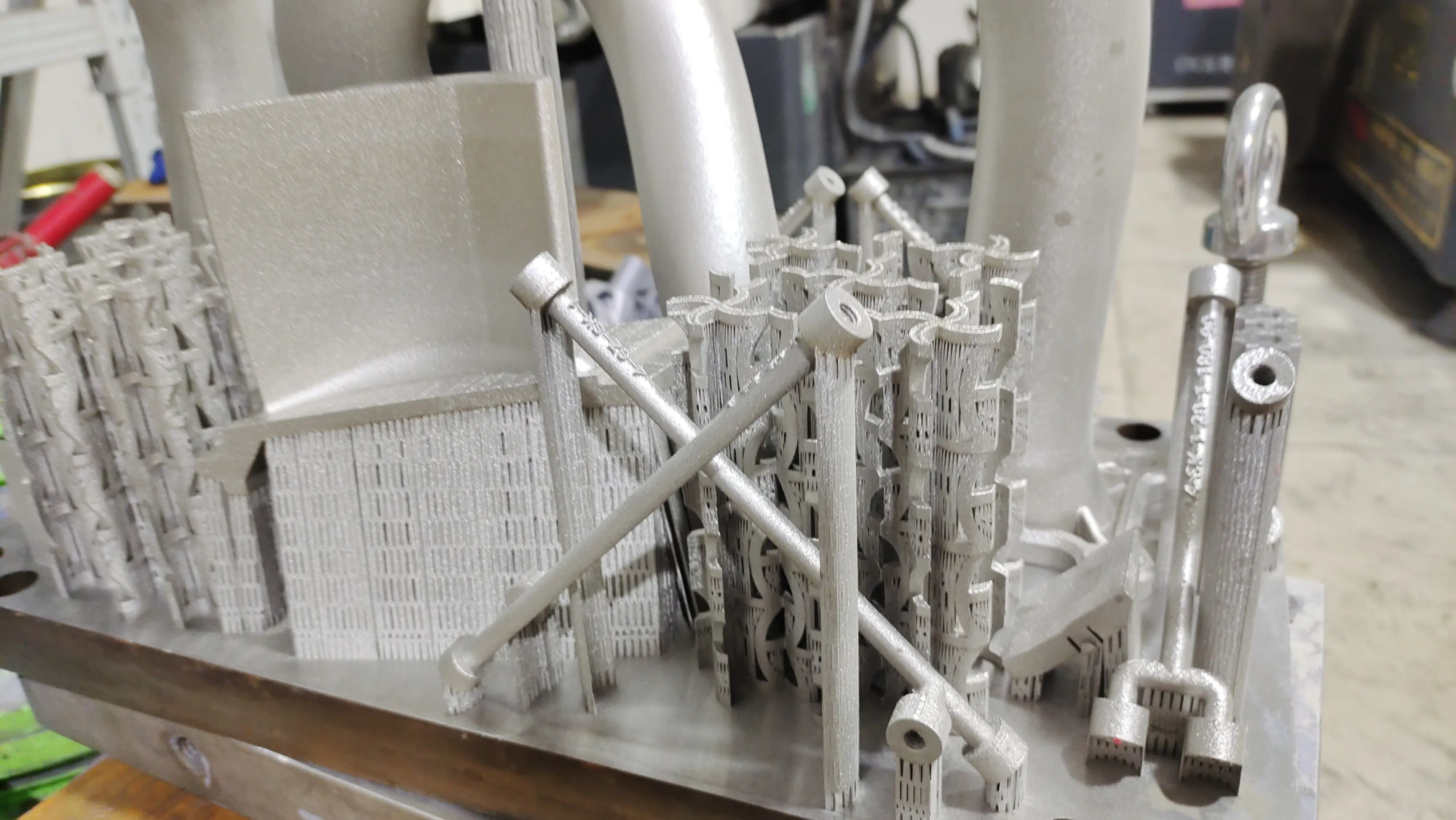
The world of 3D printing has been growing rapidly, and recent breakthroughs are changing the landscape of various industries. With the development of technology, 3D printing has become more accessible, efficient and cost-effective, opening up new possibilities for innovation and production. In this article, we will dig into the latest 3D printing breakthroughs and explore how they innovate the ways we design, manufacture and interact with products.
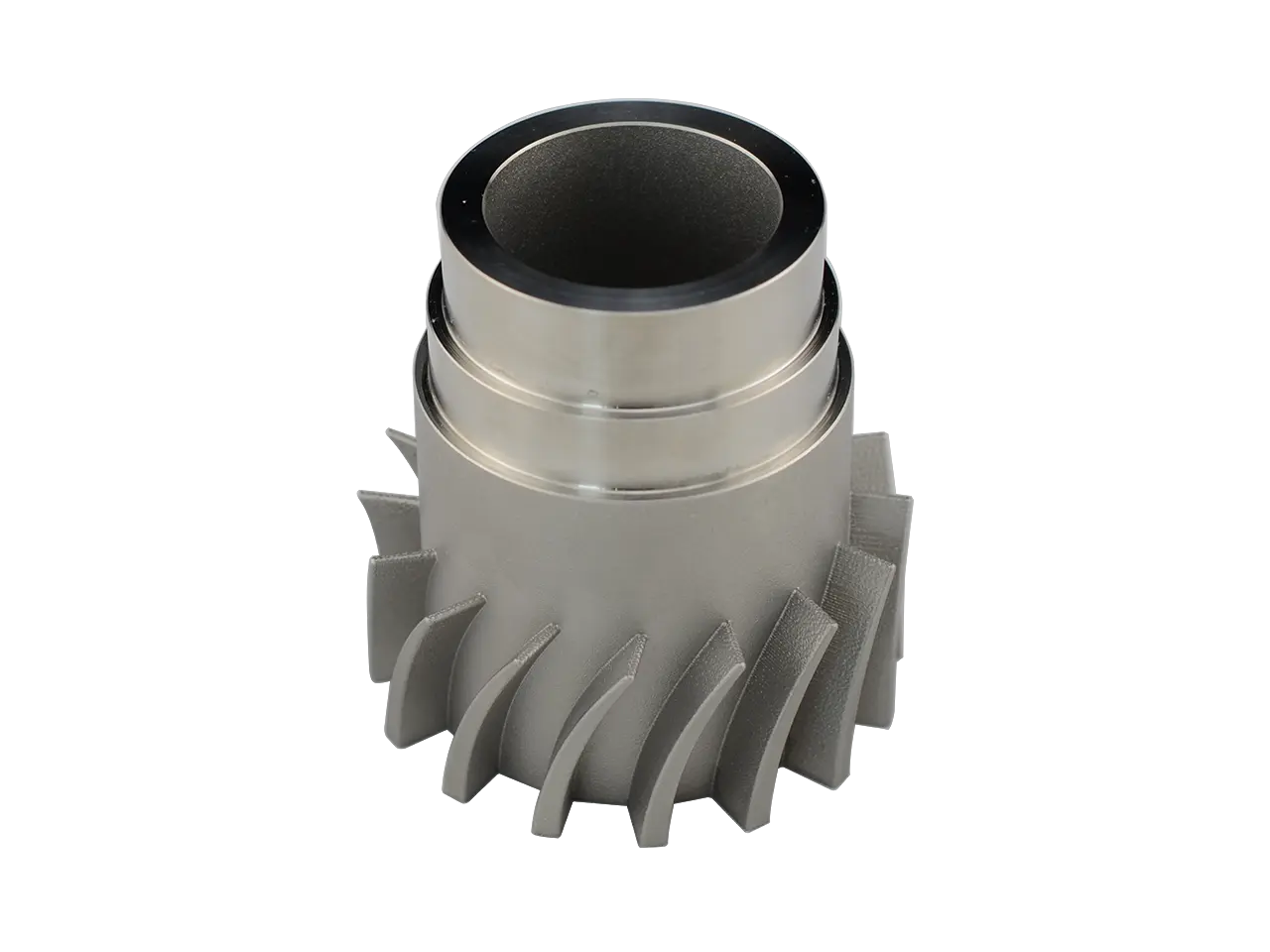
One of the most important advances in 3D printing is the development of selective laser melting (SLM) technology. SLM is an additive manufacturing process that uses high-power lasers to melt and fuse metal particles to create complex geometry and structures with unprecedented accuracy. This technology has been widely adopted in the aerospace, automotive and medical industries where high-strength, lightweight components are crucial. Companies like professional rapid prototyping manufacturer Greatlight are leveraging SLM technology to produce complex metal parts with advanced accuracy and speed.
Another major breakthrough in 3D printing is the development of advanced materials and post-processing technologies. Researchers have been working to create new materials with unique properties, such as self-healing, shape changes and adaptive materials. These materials have the potential to transform industries from healthcare to energy. In addition, advances in post-treatment technology, such as surface finishing and coating, give 3D printed parts enhanced aesthetic and functional properties.
The rise of 3D printing has also led to the development of innovative applications and business models. For example, 3D printing enables the creation of customized products such as prosthetics, implants and dental implants to be tailored to the needs of individual patients. In addition, the company is using 3D printing to produce spare parts on demand, reducing inventory costs and lead time. The technology can also create complex systems such as 3D printed batteries, fuel cells and submarines.
Furthermore, 3D printing has the potential to change our perspective on sustainability and waste management. By enabling product production, 3D printing can reduce waste and minimize the environmental impact of traditional manufacturing processes. Additionally, researchers are exploring the use of recycled materials and bioplastics in 3D printing, which could help reduce the technology’s carbon footprint.
In short, the latest 3D printing breakthrough is changing manufacturing and beyond. With the development of SLM technology, advanced materials and post-processing technologies, 3D printing is becoming an increasingly viable option for producing complex, high-performance products. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect to see new applications, business models and innovations emerge, revolutionizing the way we design, produce and interact with products.
FAQs (FAQs)
- What is 3D printing?: 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is the process of creating physical objects from digital designs by layering materials such as metals, plastics, and ceramics.
- What is SLM technology?:Selective laser melting (SLM) is a 3D printing process that uses high-power lasers to melt and fuse metal particles, resulting in complex geometry and structures with unprecedented accuracy.
- What are the benefits of 3D printing?: The benefits of 3D printing include improved accuracy, reduced material waste, faster production times, and the ability to create complex geometry and custom products.
- Which industries are using 3D printing?: 3D printing is used in various industries including aerospace, automotive, medical, healthcare, energy and consumer products.
- Can I customize my own 3D printing product?: Yes, many companies (such as Greatlime) offer customization services for 3D printing products, allowing you to make customized products based on your specific needs and demands.
- Is 3D printing environmentally friendly?:3D printing has the potential to reduce waste and minimize the environmental impact of traditional manufacturing processes, but the technology also has its own environmental footprint, which is addressed by the development of sustainable materials and practices.