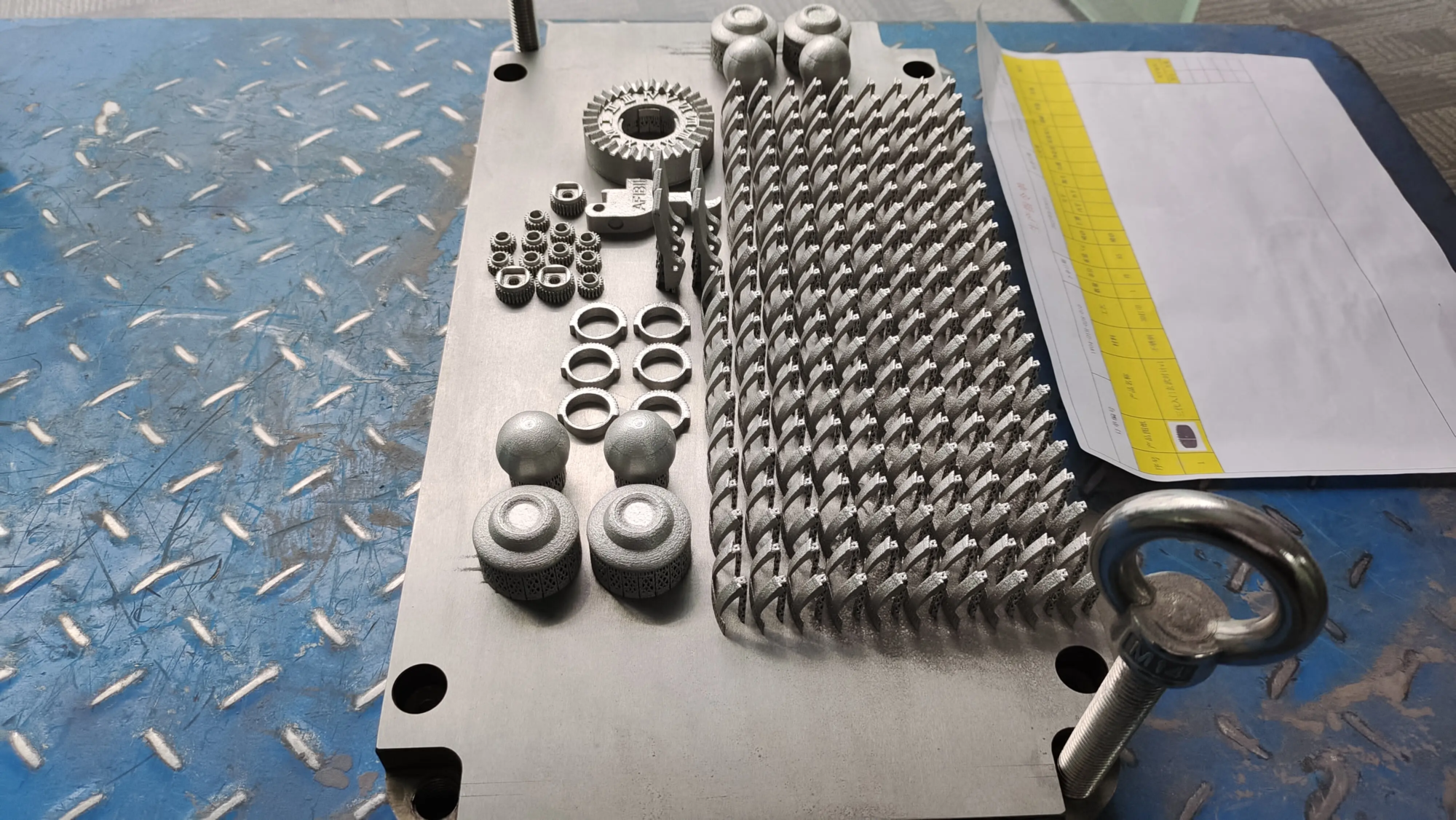
introduce
The evolution of 3D printing continues to change the industry, and audio engineering is no exception. An interesting application? 3D printed angle. Used in speakers, automotive systems, industrial sensors and wind instruments, the speaker can accurately amplify and direct sound waves. Unlike traditional manufacturing, 3D printing unlocks unprecedented design freedom, material versatility and rapid iteration. In this guide, we delve into the technical aspects of 3D printing angles, design strategies and real-world potential.
How 3D printing revolutionizes horn design
Traditional horn manufacturing relies on subtraction methods or metal casting, limiting geometric complexity and customization. 3D printing (additive manufacturing) overcomes these obstacles:
- Hyperbolic/complex geometric shapes: Create an impossible exponential curve, nested channel or helical structure for CNC machining.
- Lightweight: Optimize the internal lattice to reduce weight while maintaining rigidity.
- Integrated components: Single print embedded in a mount, flange or acoustic damper.
- Substantial-specific sound adjustments: Match material properties (density, damping) to the target frequency.
Key technologies for 3D printing horns
-
Fusion Deposition Modeling (FDM):
- Material:abs, petg, nylon.
- The best: Low-cost prototype, non-critical acoustic part or educational tool.
- limit: Layer lines may affect sound quality; limited material strength.
-
Stereo-lithography (SLA) and resin printing:
- Material: Standard, sturdy or flexible resin.
- The best: Highly determined prototype with smooth surface.
- Selective laser melting (SLM) and direct metal laser sintering (DML):
- Material:Aluminum, titanium, stainless steel, copper alloy.
- The best: The angle of end use that requires strength, thermal stability or precise acoustic performance (such as car angle).
- Advantages: Creates a completely dense, closed structure that is ideal for high-pressure sound waves.
Design principle for optimal performance
- Waveguide geometry: Smooth internal surface minimizes distortion. Avoid sharp transitions; use splines for gradual flares.
- Thick wallPlastic ≥1.5 mm; metal ≥0.8 mm to prevent vibration caused by resonance.
- Acoustic damping: Combine the grid, helmholtz resonator or viscoelastic insert to cancel unwanted frequencies.
- Support structure: Minimize internal support to simplify post-processing. Designed self-support angle > 45°.
Material Selection Guide
| Material | The best | Acoustic influence |
|---|---|---|
| ABS plastic | Prototype, budget project | Moderate damping; mid-frequency clarity |
| Nylon (PA12/PA11) | Durable lightweight corners | Balanced acoustics; impact resistance |
| Aluminum (ALSI10MG) | Automotive/sensor applications | Bright, sharp sound; high reflectivity |
| Brass (Cunisi) | Musical instruments | Rich harmonics; excellent resonance |
Acoustic accurate post-processing
The surface directly affects the propagation of sound waves. Key steps:
- Support deletion: Chemical etching of CNC or metal; solvent smooth of resin.
- polishing: Interior tumbling, electrochemical polishing (for metals) or vapor smoothing (polymer).
- seal: Coat the inner surface with epoxy resin or acoustic paint to eliminate microscopic multiples.
- Vibration test: Use a laser vibrator to detect and suppress structural resonance.
Professional tips: Cooperate with service end-to-end services – similar Greatcan provide CNC machining interface, release stress relief and custom coatings to meet MIL-SPEC tolerances.
Apply to break industry norms
- car: Customized horn array with directional focus.
- aerospace: Lightweight titanium horn for cockpit alarm systems.
- Hi-Fi audio: Copper alloy angle with fractal interior design for distortion-free treble.
- Industrial: Corrosion-resistant sensor angle of chemical plants.
Why 3D printing horns outperform traditional methods
- speed: Iterative design in a few days rather than weeks.
- cost: No tool fee; customization/small batch economy.
- Sustainability: Close to zero material waste with CNC.
- accurate: Use SLM/DML to achieve ±0.1 mM tolerance.
Challenges and solutions
- challenge: Sound scattering caused by layers.
Solution: Optimize printing direction; use steam polishing (polymer) or thermal isostatic pressure (metal). - challenge: Material limitations for high SPL (sonic pressure level) applications.
Solution: Injected copper alloy or carbon fiber composite material.
Great Advantages: Your Companion Precision Horn
exist GreatWe use Industrial SLM/DMLS technology Solve complex rapid prototyping challenges. With expertise in metal additive manufacturing and one-stop post-treatment, we offer:
- Material freedom: Titanium, aluminum, inconel, copper alloy and composite materials.
- End-to-end service: From topologically optimized design to CNC Trimmed finish.
- Speed and scale: Rush prototypes within 48 hours; competitively priced batches.
As Leading fast prototype companies from ChinaWe serve Fortune 500 customers across the automotive, aerospace and audio sectors. Customize your precision speaker components now Greglight’s platform With unparalleled quality and affordability.
in conclusion
The 3D-printed horn represents a symphony of engineering innovations – combining acoustics, materials science and additive manufacturing. They can make lighter, smarter, and more efficient sound systems from concert halls to self-driving cars. Professional SLM/DMLS service when DIY printing is suitable for prototyping Great Unlock industrial-grade reliability. As materials and printers develop, further breakthroughs in sound loyalty and design activism are expected.
FAQ
Q1: Can 3D printed horns match the sound quality of molded or processed angles?
one: Yes, with the best design and professional post-treatment, especially with metal SLM. Surface polishing and precise geometry prevent distortion.
Q2: How do metal angles compare to plastic angles?
*A: **Metals such as brass/aluminum provide brighter resonance sounds, which are ideal for high frequencies. Plastics (for example, nylon) suppress vibration and are suitable for mid-range applications.
Q3: Which file format is best for Horn Design?
*A: ** Steps of CAD export or IGES. Ensure the printing of watertightness STL ≤0.01 mm.
Q4: Are 3D printed horns weather-resistant?
one: Metal corners are essentially strong. For polymers, ultraviolet resin (ASA) or nylon with sealant can withstand outdoor use.
Q5: Will Greatlight handle small batch production?
*a: ** is – from a single prototype to thousands of units. We support low-mix, high-volume scaling at a competitive rate.
Q6: How long does it take to print a metal speaker?
*A: **A 6-inch aluminum speaker takes about 20 hours to print. With post-processing, Greatlight expects 3-5 days.
Question 7: Can I use 3D printing with traditional manufacturing?
*A: **Absolute. Greatlight offers hybrid workflow-EG, 3D printed horn with CNC-machined brass throat.
Change your acoustic projects with innovation – Explore Greatlight’s rapid prototype solutions.