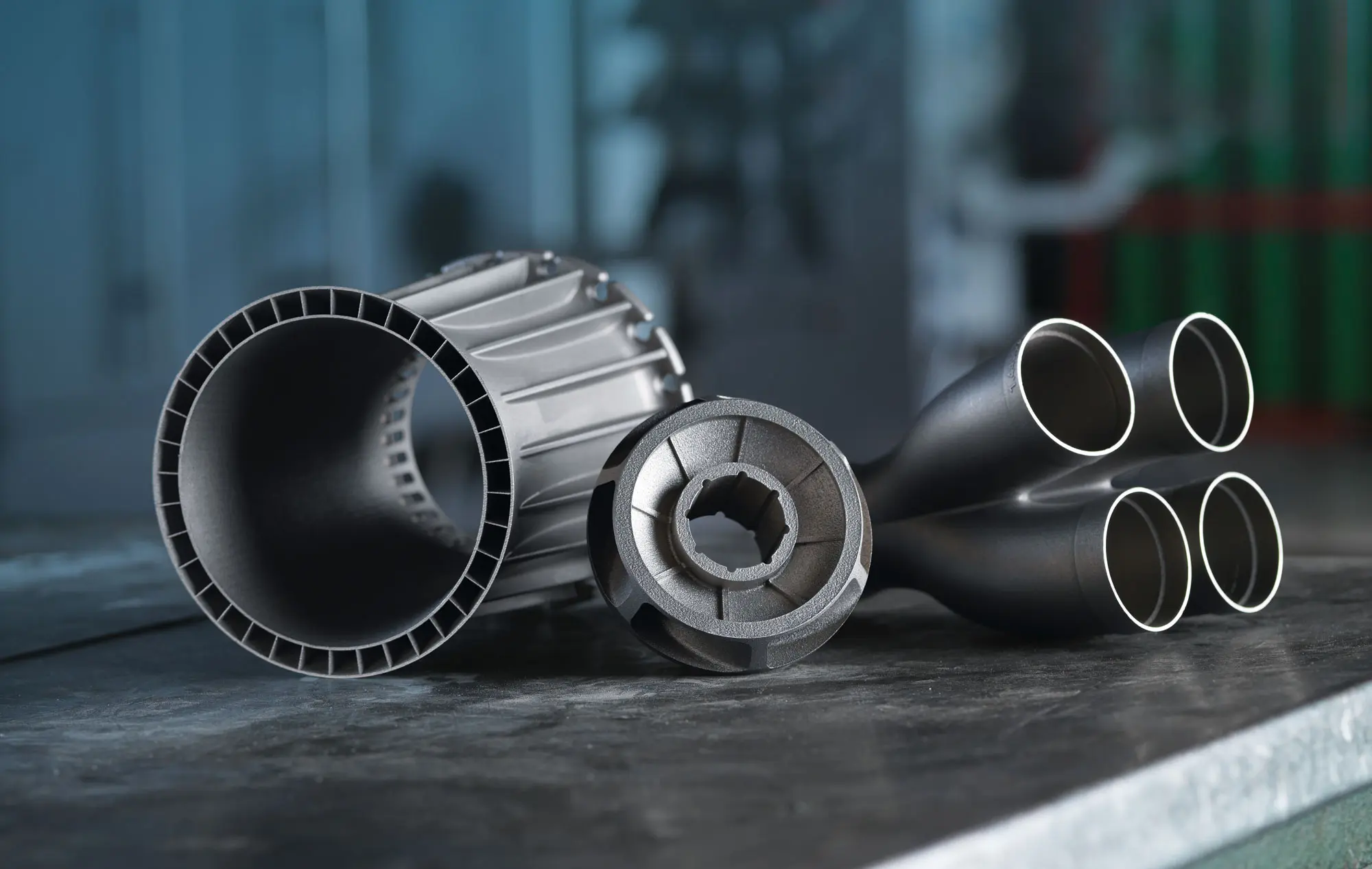
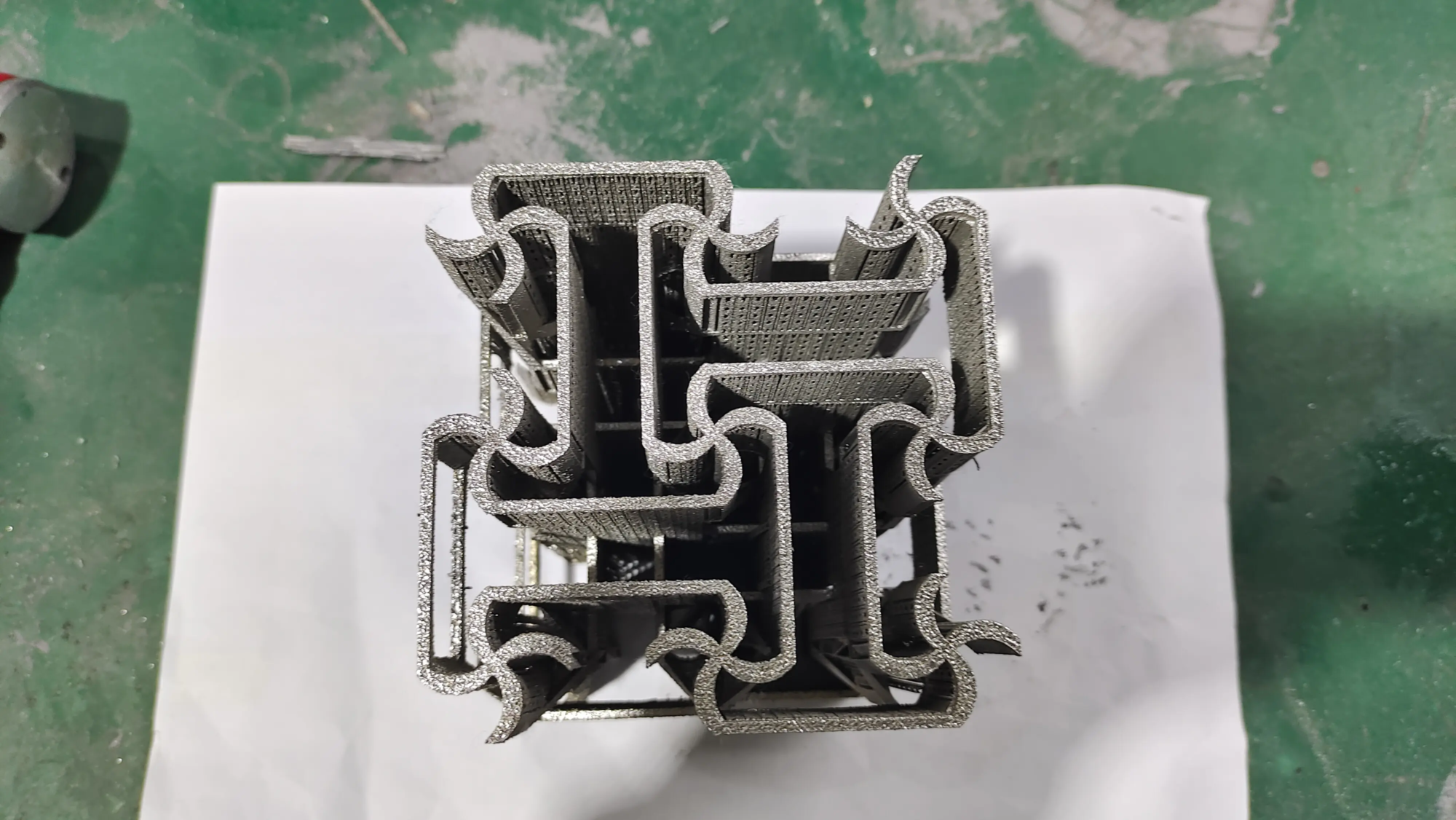
The advent of 3D printing technology revolutionized the manufacturing industry, thus creating complex geometric shapes and structures that were previously unproductive. Among the various materials used in 3D printing, titanium has attracted great attention due to its special strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. In this article, we will dig into the world of 3D printed titanium and explore its benefits, challenges and applications.
Benefits of 3D printing of titanium
Due to its unique characteristics, titanium is an ideal material for 3D printing. It is 45% lighter than steel, but has similar strength, making it an excellent choice for aerospace, medical and automotive applications. In addition, the high corrosion and biocompatibility of titanium make it suitable for implants, surgical instruments and other medical devices. The ability to 3D print titanium also allows the creation of complex geometric shapes, such as lattice structures, which can enhance the mechanical properties of the material.
The Challenge of 3D Printing Titanium
Despite the benefits of 3D printing of titanium, there are some challenges in this process. One of the main challenges is the high cost of titanium powder, which can make the printing process expensive. Furthermore, the high reactivity of titanium and its affinity to oxygen may lead to porosity and oxidation, which impairs the mechanical properties of the material. To overcome these challenges, specialized 3D printing equipment, such as selective laser melting (SLM) machines, are needed. These machines use high-power lasers to melt and fuse titanium powder, resulting in dense and intense printed parts.
Application of 3D printing of titanium
3D printing titanium has a wide range of applications. In the aerospace industry, 3D printed titanium components are used in aircraft and spacecraft due to their high strength to weight ratio and corrosion resistance. In the medical field, 3D printed titanium implants such as hip and knee replacements are used due to their biocompatibility and ability to promote bone growth. The automotive industry can also benefit from 3D printing of titanium and use it to create lightweight components such as engine parts and exhaust systems.
Post-processing and completion of services
After 3D printing of titanium, post-processing and finishing services are often required to enhance the properties of the material and achieve the desired finish. These services may include heat treatment, processing and polishing. Heat treatment can be used to relieve residual stress and improve the mechanical properties of the material, while machining can be used to achieve tight tolerances and complex geometry. Polishing can be used to create a high-gloss finish, reduce friction and improve the corrosion resistance of the material.
in conclusion
In short, 3D printed titanium is a rapidly developing field with huge innovation and growth potential. The benefits of 3D printing of titanium, including its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance and biocompatibility, make it an ideal material for a wide range of applications. Despite challenges such as high cost and porosity, advances in 3D printing equipment and post-processing technologies are constantly improving the quality and affordability of 3D printed titanium alloys. As the industry continues to grow, we can expect an increase in adoption of 3D printed titanium in areas ranging from aerospace and medical to automotive and beyond.
FAQ (FAQ)
Q: How much does 3D printing of titanium cost?
A: The cost of 3D printing of titanium may vary depending on the complexity of the design, the size of the components, and the equipment used. However, on average, the cost of 3D printing of titanium ranges from $500 to $500 per kilogram.
Q: What are the benefits of 3D printing of titanium for traditional manufacturing methods?
A: The benefits of 3D printing of titanium include the ability to create complex geometric shapes, reduce material waste and improve the mechanical properties of the material.
Q: What are the common applications of 3D printing of titanium?
A: Common applications of 3D-printed titanium include aerospace, medical, automotive and industrial components such as implants, surgical instruments, engine parts and exhaust systems.
Q: What post-processing techniques can be used to enhance the characteristics of 3D printed titanium?
A: Post-treatment techniques such as heat treatment, machining and polishing can be used to alleviate residual stress, improve mechanical properties and achieve high-gloss effects.
Q: Is 3D printed titanium biocompatible?
A: Yes, 3D printed titanium is biocompatible and can be used in medical implants and surgical instruments due to its corrosion resistance and ability to promote bone growth.